For businesses that operate on both the web as well as physical locations, including a Google Map of your location is a great way to make sure that your customers can find you. However, including dynamic maps can also dramatically affect your website’s performance. W3 Total Cache Pro gives you the best way to include maps on your site without hurting your site’s speed.
In this test, using the Lazy Load Google Maps feature added +10 points on mobile devices to the Google PageSpeed Performance score! Review the testing results to learn how to use the Lazy Load Google Maps tool.
Upgrade to W3 Total Cache Pro and improve your PageSpeed Scores today!
Why do I need to Lazy Load Google Maps?
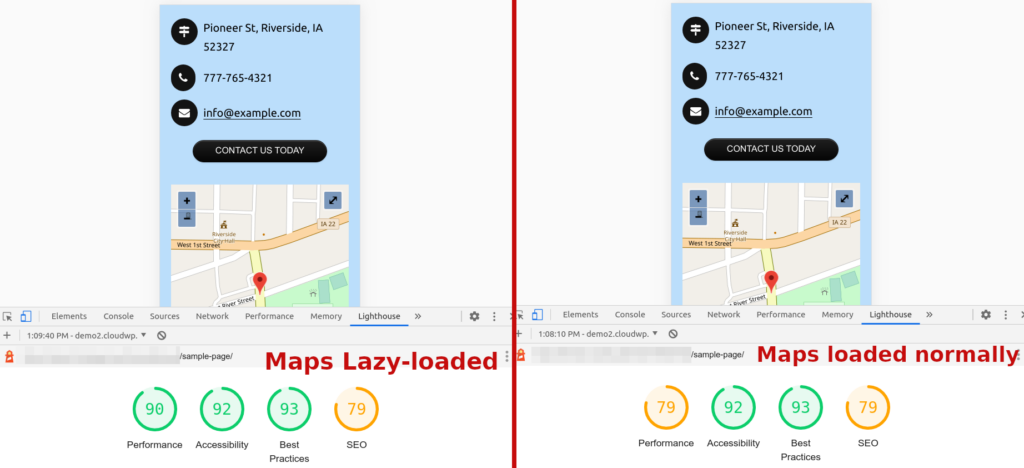
If you’re using maps, lazy loading them can increase performance dramatically. In the example above, the same page was tested with lazy loading enabled for maps, and with it disabled. This resulted in an increase in the Lighthouse performance score of 11 points.
For pages with more than one map, the score increase can be even more impressive.
How do I Use Lazy Loaded Maps?
W3 Total Cache Pro integrates with three of the most popular Google Maps plugins:
- WP Google Maps (400K+ Active Installations, 4.7/5 Star Reviews)
- WP Google Map Plugin (90K+ Active Installations, 4.2/5 Star Reviews)
- Google Maps Easy (40K+ Active Installations, 4.7/5 Star Reviews)
To enable lazy-loading Google Maps, simply navigate to Performance > User Experience and check the box to enable your plugin.
How to tell if your maps are lazy loading
- Navigate to the Webpage: Open your preferred web browser and navigate to the webpage where the Google Map is embedded.
- Open the Browser Console: Open the browser’s developer console. Typically, you can open the developer tools by pressing
F12orCtrl+Shift+I(on Windows/Linux) orCmd+Option+I(on macOS). - Select the Network Tab: Locate and select the “Network” tab. This tab shows information about network requests made while loading the page, including requests for resources like images, scripts, stylesheets, etc.
- Observe Network Requests: As you scroll down the page, keep an eye on the number of requests being made. As you reach the section containing the Google Map, if the map is lazy loaded, you should see new network requests being made as the map is loaded onto the page.If you examine the new requests being made you should be able to see icons and images used for the map in the list and hovering over the initiator in the Chrome developer tools should show links to the Google maps API.If you aren’t seeing any new requests being made it’s likely that your map is not lazy loading.
Upgrade to W3 Total Cache Pro to Enable Lazy Load Google Maps
When you upgrade to W3 Total Cache pro, you’ll not only be able to increase the performance of your Google Maps, but you’ll get access to tons of other great performance features, including Defer Render-Blocking CSS, Full Site CDN Delivery, WPML integration, and many more. Upgrade today.
In this test, using the Lazy Load Google Maps displayed a 72% decrease on the Total Blocking Time Performance score on mobile devices! Review the testing results to learn how to use the Delay Scripts tool.
Upgrade to W3 Total Cache Pro and improve your PageSpeed Scores today!
FAQ
Are Google Maps lazy loaded by default?
If you’re looking at a Google Map and click the share button, you’ll see that the iframe code includes loading=”lazy”. Many browsers support this iframe lazy loading feature.
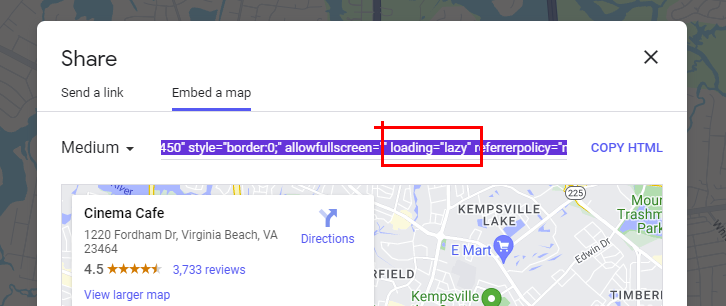
However, if you’re using a WordPress plugin to add a map to your website, those plugins don’t always use iframes and load load maps. W3 Total Cache’s Pro Feature, Lazy Load Google Maps, allows you to lazy load google maps added by some of the most popular Google Maps plugins.
Why would someone use a plugin to add a map?
There are several reasons why someone might prefer using a WordPress plugin to add a Google Map to a page instead of embedding it directly using an iframe.
Ease of Use:
Plugins often provide a user-friendly interface within the WordPress dashboard, making it easy for users who may not be comfortable with HTML or iframes to add a map.
Customization:
WordPress plugins for maps often come with additional customization options. Users can set markers, customize map styles, and configure various settings without directly dealing with code.
Maintenance and Updates:
Using a plugin means that updates and maintenance are typically handled through the WordPress dashboard, simplifying the process for users who may not be familiar with the technical aspects of web development.
How does google maps affect core web vitals?
Google Maps can significantly impact Core Web Vitals, particularly the Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This metric measures the time it takes for the largest content element in the viewport to become visible. Embedding a Google Map can increase the LCP time, as maps are often large elements that take longer to load compared to other content on the page.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): This metric measures the stability of the page layout as it loads. Google Maps can contribute to layout shifts if the map’s size or position changes as other page elements load, or if the map is loaded asynchronously without reserving sufficient space for it in the layout.
Is lazy loading google maps the same as caching google maps?
Lazy loading and caching are two distinct techniques used to optimize web performance, and they are unrelated in the context of Google Maps:
- Lazy Loading: This technique involves deferring the loading of resources until they are needed. For Google Maps, lazy loading means that the map is not loaded when the page initially loads. Instead, it is loaded only when the user scrolls to the section of the page where the map is located or when a specific interaction triggers the loading of the map. This can reduce the initial load time of the page and improve metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP).
- Caching (in the context of Google Maps): Caching in Google Maps refers to storing certain data like map images, search history, and directions on your device. This is done to speed up the loading of maps and reduce data usage in the Google Maps app. Clearing the cache in Google Maps involves deleting this stored data, which can free up space and resolve potential issues with the app.
In summary, lazy loading is a web optimization technique that delays the loading of the map until it’s needed, while caching in the context of Google Maps refers to storing map data on a device to improve the performance of the Google Maps app. The two concepts are unrelated and serve different purposes in different contexts.
W3 Total Cache
You haven't seen fast until you've tried PRO
Full Site CDN + Additional Caching Options
Advanced Caching Statistics, Purge Logs and More
Everything you need to scale your WordPress Website and improve your PageSpeed.
